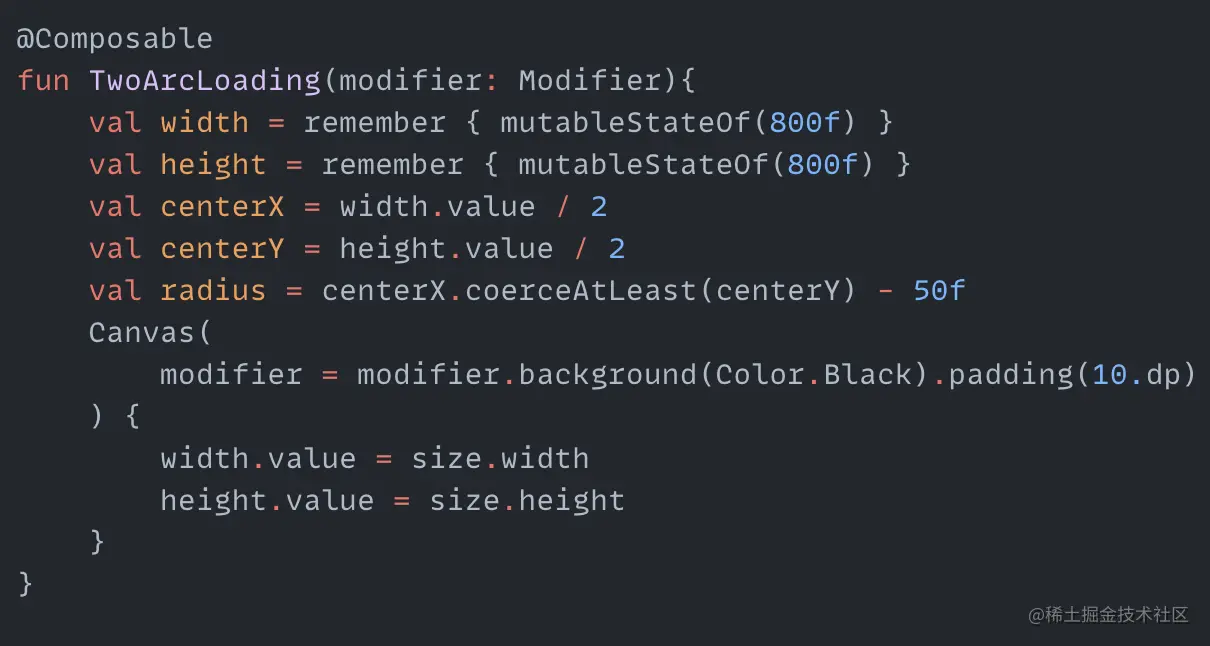
Through the previous article, we have initially learned how to use Compose to make loading animations. To consolidate this knowledge, in this article we will continue to use Compose to make a few more loading animations and deepen the impression. The article is relatively long and you can choose the animations you are interested in to read. Arcs and Circles I don't know what to call this animation, so I just named it randomly. The whole animation process is still quite simple. It consists of two parts: one part is two arcs revolving around the center at speeds from fast to slow, and the other part is a hollow circle in the center whose radius is oscillating between lengthening and shortening in a loop. So basically two cyclic animations can complete it. First we need to define the variables needed for the animation: centerX and centerY are the coordinates of the center of the animation, radius is the radius for drawing the two arcs. Then we create a cyclic animation with values from 0 degrees to 360 degrees: Here we use FastOutSlowInEasing for the speed variation to make the arcs rotate from fast to slow. Next we draw the two arcs in Canvas: Just draw two fan shapes, and add the angleDiff change value to startAngle. The two arcs can rotate. The effect is as follows: Next is the expanding and contracting hollow circle in the middle, which is also a cyclic process. We create another cyclic animation with the range oscillating between 20f and 60f: circleSize is the radius…
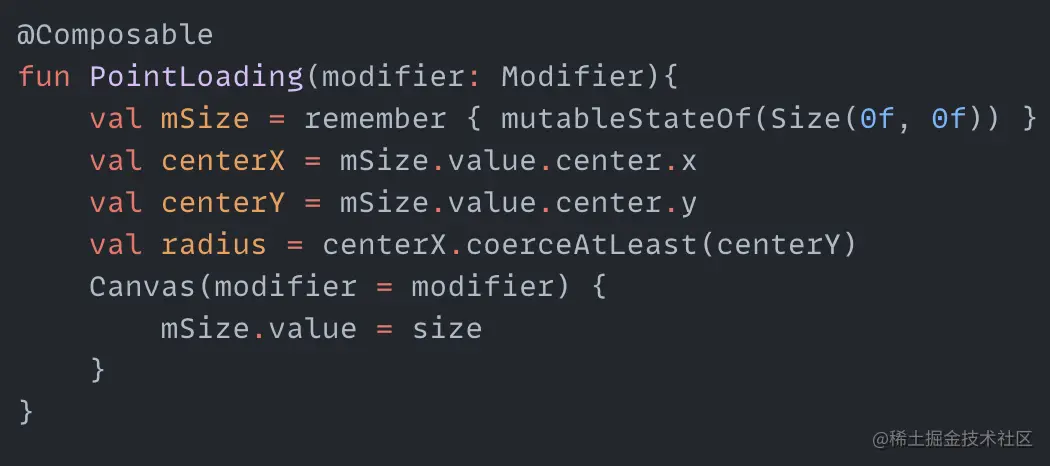
Spinning dots I've seen elsewhere online where someone used CSS to create an effect with several dots spinning around the center, each dot sequentially changing in size and transparency. Since CSS can do this, can we create a similar effect using Compose? Let's give it a try. First, since the dots spin around the center, we need to determine the coordinates of the center point and the radius. In the code, centerX and centerY are the coordinates of the center point, radius is the radius of the circle, and mSize gets the canvas size to dynamically update the center point coordinates and radius. We also need a set of angles - these angles will be used to draw the dots around the circumference. angleList stores the angles for drawing each dot. With these angles, we can use the sine and cosine formulas to calculate the center point coordinates for each dot: pointX and pointY are the functions to calculate the center point coordinates for each dot. Using this, we can first draw a circle of dots around the circumference. Now that we've drawn the dots, how do we make them spin and change size and transparency? We can think of this process as continuously changing the size and transparency of each dot as it is drawn. So we can create two more arrays to store the changing radius and transparency values. When drawing each dot, we can use an animation loop to pull values for each dot from the radius and alphaList arrays. This will create the change in size…
Preface For Android applications, especially large applications, build time is a headache. Build times of several minutes or even tens of minutes are intolerable for most developers. What we face most in actual development is local incremental compilation. Although the official has done some processing on incremental compilation, the actual effect is not ideal, especially in specific projects, particularly medium and large projects. Background Currently NetEase Cloud Music and its subordinate look live broadcast, xinyu, mus and other app have successively adopted the aar of public modules, using the latest agp version and other measures, but the overall build time is still long, incremental build is generally 2-5 min. Since I am currently mainly responsible for the development of mus business, I have done some optimization work on incremental builds based on the current build situation of mus. Time Consuming Investigation Combining with the specific situation of mus construction, the main focus of the current build time consumption is concentrated in some Transform and dexMerge (agp version 4.2.1). For Transform, the main consumption is from some tools like privacy scanning, automated buried points and so on, usually the build time of these Transform has reached several minutes incrementally. In addition, the dexMeger task is also a big head during incremental builds. The incremental dexMerge build time for mus is about 35-40s, and the incremental build dexMerge time for NetEase Cloud Music is about 90-100s. Optimization Direction For large projects, basically the most time-consuming is Transform. These Transform generally fall into the following two categories: Functional Transform, removing only affects its…
As a developer, performance optimization is an unavoidable topic that we will certainly encounter during daily development. Android performance optimization is actually quite mature, with mature routines, mature methodologies, mature open source frameworks, etc. For developers with less experience in performance optimization, there may be few opportunities to learn or summarize these mature routines, methodologies, or frameworks. So as a developer who has been doing performance optimization for many years, I will summarize some of the methodologies in this article for everyone's reference. The Essence of Performance Optimization First, let me introduce the essence of performance optimization. My understanding of its essence is: The essence of performance optimization is the reasonable and sufficient use of hardware resources to make the program perform better. And the purpose of the program performing better is to gain more retention, usage time, reputation, profit and other returns from customers. So based on the essence, the two most important things about performance optimization are: Reasonable and sufficient use of hardware resources Make the program perform better and gain returns Let's talk about these two things below. Reasonable and Sufficient Use of Hardware Resources Sufficient means making full use of the resources of the hardware, but sufficient is not necessarily reasonable. For example, we suddenly opened hundreds of threads at once, the CPU was fully utilized, but it was not reasonable. So reasonable means that the hardware resources exploited can have a positive effect on the performance of the program. Hardware resources include: CPU, memory, disk, battery, traffic (not a hardware resource, but also one of…
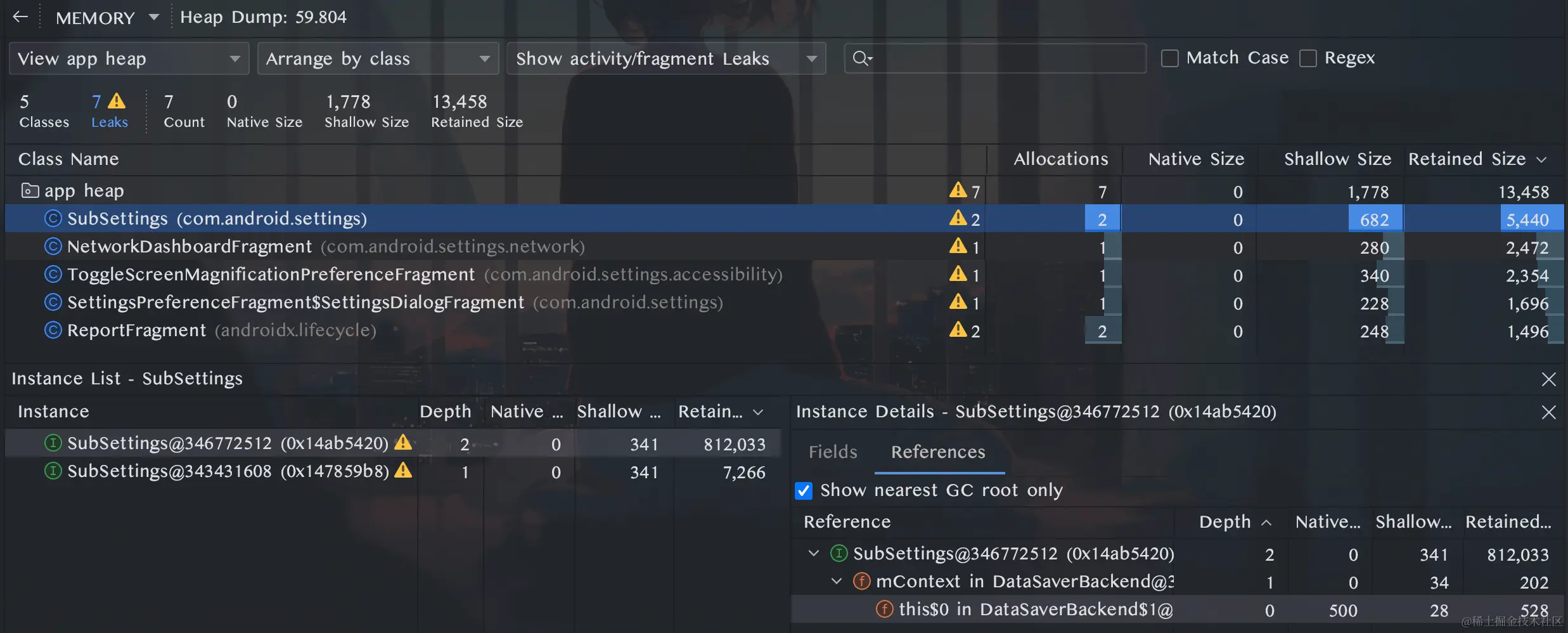
Analysis Idea Memory leak refers to the phenomenon where some objects are no longer in use in the Android process, but are referenced by some longer-lived objects, causing the occupied memory resources to fail to be recycled by GC, and memory usage continues to increase. Memory leaks are a common factor leading to decreased performance and lag in our applications. The core ideas for solving such problems can be summarized in two steps: Simulate memory leak operations, observe changes in the application Heap memory, and determine the approximate location of the problem; Expand the analysis for the specific location, find the complete reference chain from the leaked object to the GC Root, and fix the memory leak from the source. Analysis Tool: Android Studio Profiler The commonly used memory analysis tools in Profiler are two: Memory Chart and Heap Dump. The memory curve can observe the memory usage status in real time to assist us in performing dynamic memory analysis. A typical phenomenon of memory leaks in the memory curve is a ladder-like shape. Once it rises, it becomes difficult to decrease. For example, after an Activity leak, repeatedly opening and closing the page, the memory usage will keep rising, and after clicking the trash can icon to manually GC, the usage cannot decrease to the level before opening the Activity. At this point, it is highly likely that a memory leak has occurred. At this time, we can manually dump the memory distribution in the application heap at that moment for static analysis: UI indicator descriptions: Allocations: Number of…
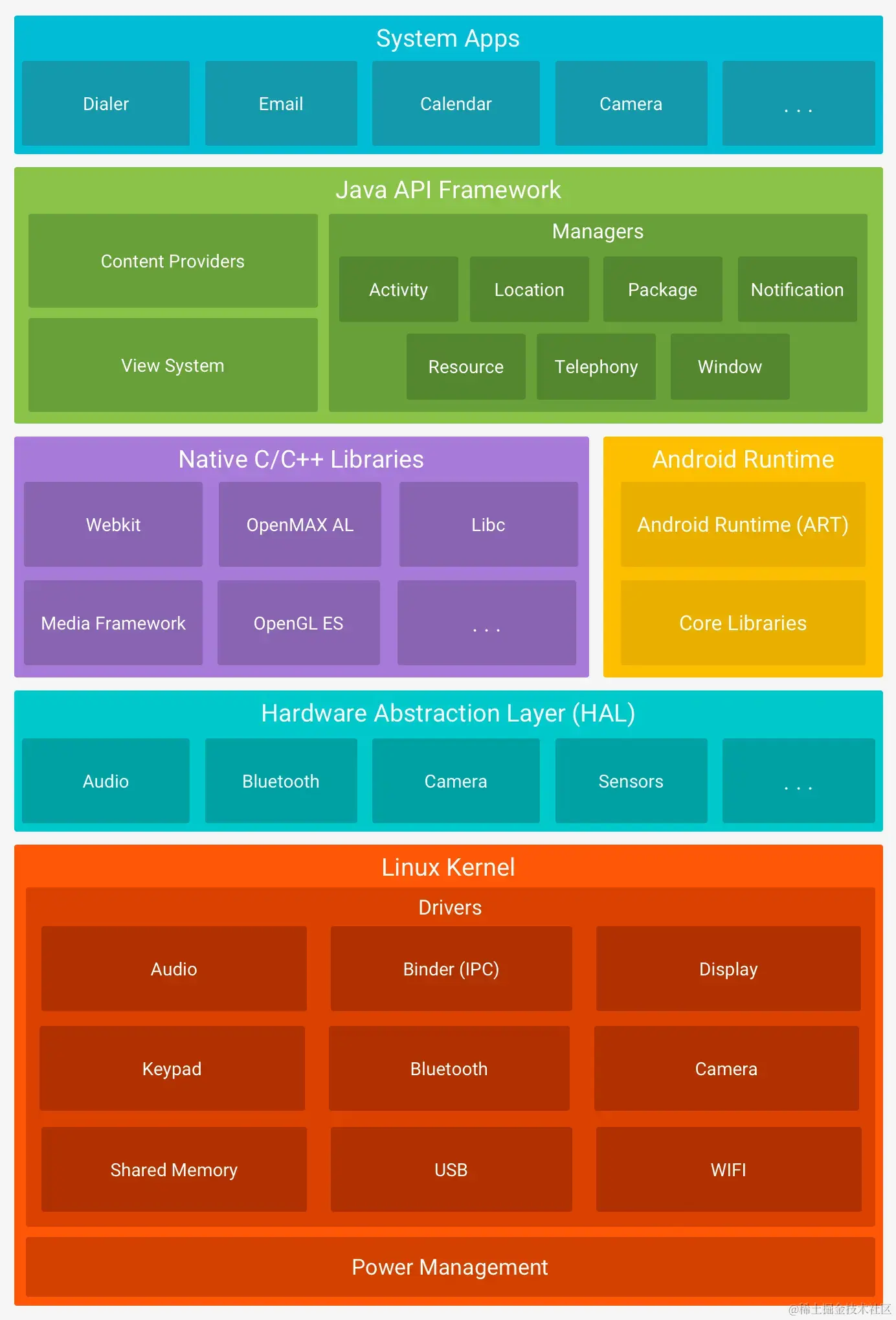
The figure above is the overall architecture of Android. Android Runtime is to Android what the heart is to the human body. It is the environment where Android programs are loaded and run. This article mainly focuses on the Android Runtime part and explores the development and current status of Android Runtime. It also introduces the feasibility of using Profile-Guided Optimization (PGO) technology to optimize application launch speed. Evolution of App Runtime JVM Native Android code is written in Java or Kotlin and compiled into .class files by javac or kotlinc. Before Android, these .class files would be input into the JVM for execution. The JVM can be simply divided into three subsystems: Class Loader, Runtime Data Area, and Execution Engine. Among them, the Class Loader is mainly responsible for loading classes, verifying bytecode, linking symbol references, allocating memory for static variables and static methods, and initializing them. Runtime Data is responsible for storing data, divided into method area, heap area, stack area, program counter, and native method stack. The Execution Engine is responsible for executing binary code and garbage collection. In the Execution Engine, Interpreter or JIT execution is used. Interpreter means interpreting the binary code during execution. Interpreting the same binary code each time is wasteful, so hot binary code will be JIT compiled into machine code for faster execution later. DVM (Android 2.1/2.2) JVM is a stack-based runtime environment. Mobile devices have higher requirements for performance and storage space, so Android uses the register-based Dalvik VM. To convert from JVM to DVM, we need to convert .class…
Summary: How to slim down APKs is an important optimization technique for Android. Both installation and updating of APKs require network downloading to devices, and the smaller the APK, the better the user experience. Through detailed analysis of the internal mechanisms of APKs, the author provides optimization methods and techniques for each component of APKs, and implements a minimization process for a basic APK. Body: In golf, the player with the lowest score wins. Let's apply this principle to Android app development. We will play with an APK called "ApkGolf", with the goal of creating an app with the smallest number of bytes possible that can be installed on a device running Oreo. Baseline Measurement To start, we generate a default app using Android Studio, create a keystore, and sign the app. We then use the command stat -f%z $filename to measure the number of bytes of the generated APK file. Furthermore, to ensure the APK works properly, we install it on a Nexus 5x phone running Oreo. Looks good. But now our APK size is close to 1.5Mb. APK Analyser Considering our app's functionality is very simple, the 1.5Mb size seems bloated. So let's dig into the project to see if there are any obvious areas we can trim to immediately reduce the file size. Android Studio generated: A MainActivity extending AppCompatActivity; A layout file using ConstraintLayout as the root view; Value files containing three colors, one string resource, and one theme; AppCompat and ConstraintLayout support libraries; An AndroidManifest.xml file; PNG format launcher icons, square, round, and foreground. The…